Multilateration (MLAT) Overview
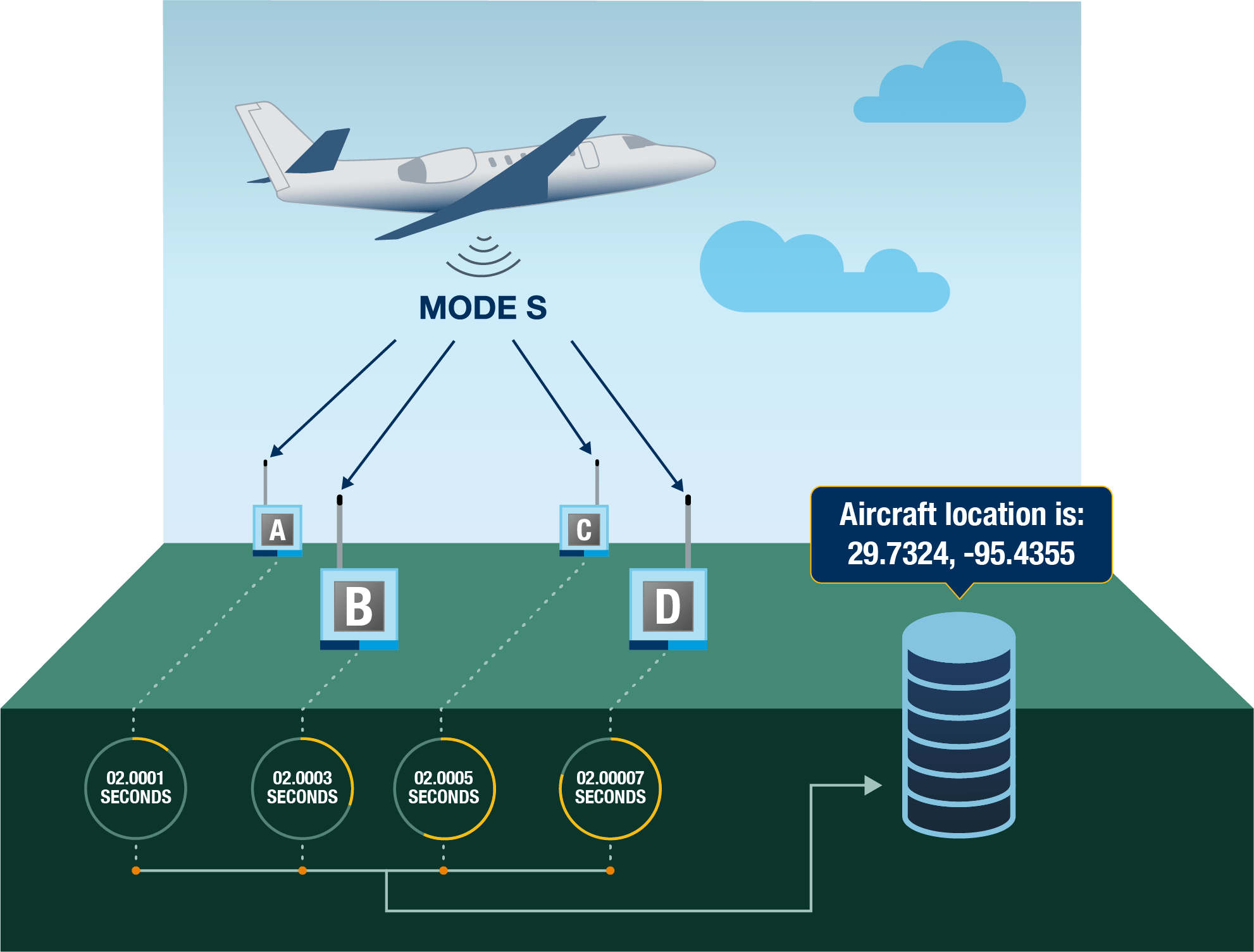
Aircraft without ADS-B transponders do not broadcast their latitude/longitude, so FlightAware uses multilateration of 1090 MHz Mode S transponder signals to determine the aircraft's location by using time difference of arrival (TDOA) when an aircraft is detected across four or more receivers/ground stations. (Technically, multilateration can be accomplished with only three receivers but for improved accuracy and reliability FlightAware requires four.) Using MLAT, FlightAware can take the aircraft's transponder-provided identification and altitude, then determine the latitude/longitude, and provide real-time flight tracking.
Because an aircraft must be within line-of-sight of four or more FlightAware receivers, MLAT is only available inside a subset of our ADS-B coverage footprint. MLAT positions are effectively real-time, although calculation delays and processing latency is generally 4-6 seconds. FlightAware currently emits up to six MLAT positions per minute per aircraft on the web site.
How it worksMLAT-enabled receivers keep the FlightAware server up to date on which Mode S aircraft are being received. When a particular aircraft is being received from four or more receivers, the server requests sufficient Mode S data from the receiver to sync the time and multilaterate the position of the aircraft. An MLAT-enabled feeder will use approximately 50 Kbps of upstream bandwidth while actively contributing to MLAT flight tracking.
Improving Availability of MLAT flight tracksBoth PiAware (v2.0 and above) and FlightFeeder (v7.0 and above) ground stations can currently participate in MLAT. Deploying more receivers in an area will directly improve the ability for FlightAware to generate MLAT positions. For optimal coverage, receivers should be 10-150 km apart and in a triangular, square, or circular pattern -- not in a straight line like along a road. Recruiting other people in your general area to host new PiAware or FlightFeeder sites is the best way to grow the availability of FlightAware's MLAT network. As of 2025年 07月 4日 (星期五), 30,028 receivers are connected and capable of producing MLAT data (view more receiver stats).
Multilateration (MLAT) flight tracking on FlightAware.com
When available, FlightAware's MLAT positions of Mode S aircraft can be seen in the track log alongside regular RADAR, datalink, and projected positions.
For example:
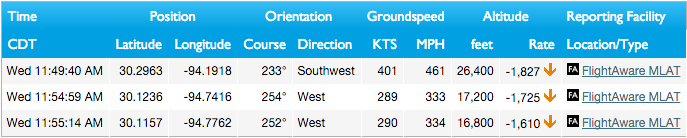
MLAT flight tracking in SkyAware
For people running PiAware or hosting a FlightFeeder, FlightAware automatically feeds MLAT-derived positions to your SkyAware web interface for live MLAT tracking of Mode S aircraft that your receiver and antenna can see. MLAT aircraft are depicted on the map and the chart in light orange. Use of the MLAT results provided by FlightAware is subject to specific terms.